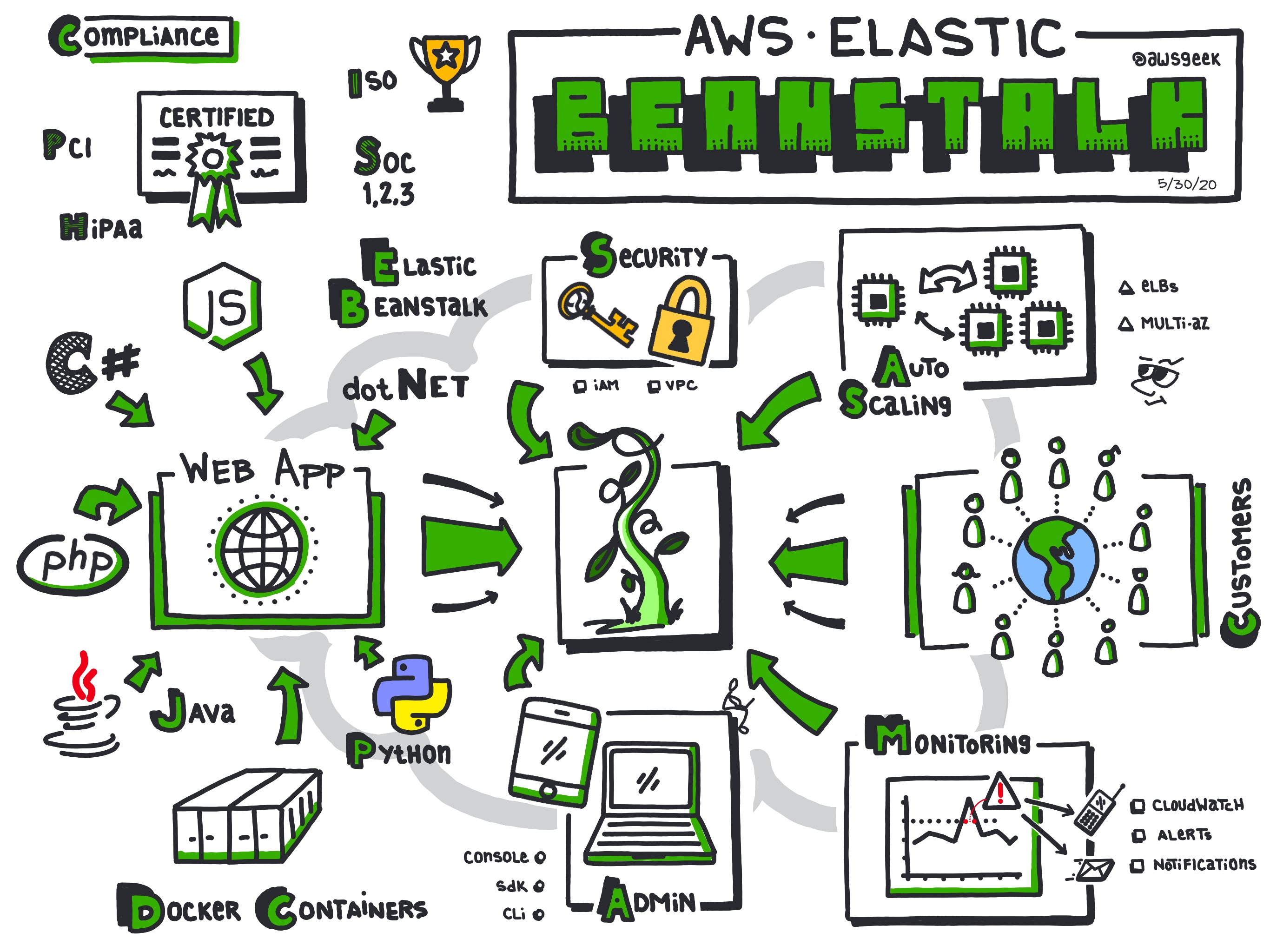
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering from Amazon Web Services that facilitates the deployment and management of applications in the cloud. It abstracts much of the underlying infrastructure complexity, allowing developers and IT administrators to focus on writing code without the necessity to manage server provisioning, scaling, or load balancing manually. Elastic Beanstalk supports widely-used programming languages such as Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker, making it versatile for various application projects.
Use Cases
Elastic Beanstalk is frequently used for deploying scalable web applications and services. It's an ideal choice for developers who want to deploy web apps quickly with minimal configuration. Applications that require automatic scaling based on demand can leverage Elastic Beanstalk's Auto Scaling capabilities. It suits companies looking to deploy microservices and containerized applications with Docker. Developers can also use it for testing applications and determining performance under different configurations due to the ease of managing environments.
Pricing
Using AWS Elastic Beanstalk itself does not incur additional costs beyond the AWS resources consumed by the deployed application, such as EC2 instances, Elastic Load Balancing, or RDS. Billing is based on the actual AWS resources deployed within the environment, which makes it attractive for environments that demand cost-effectiveness. Users must monitor the utilization of associated AWS resources to manage costs efficiently.
Scalability
One of Elastic Beanstalk's strengths is its ability to scale applications seamlessly. It can automatically adjust to load requirements by scaling resources up or down based on user-defined triggers and thresholds. The Auto Scaling feature, combined with Elastic Load Balancing, ensures that applications can handle varying levels of demand without manual intervention. This dynamic scaling helps maintain performance and availability while optimizing resource use.
Availability
Elastic Beanstalk offers high availability through its integration with other AWS infrastructures, like deploying applications across multiple Availability Zones in a region. Each deployed application benefits from AWS’s global network of data centers, offering redundancy and resilience across the infrastructure. Users can configure their environments to promote high availability, such as setting up load balancing and health monitoring.
Security
AWS Elastic Beanstalk integrates multiple AWS security services to deliver a secure environment. It supports AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for controlling access to environments and resources. Users can use Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to provide networking security and isolate resources. Elastic Beanstalk also supports Secure Socket Layer (SSL) for data encryption in transit and AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for managing encryption keys. Regular security updates are rolled out to ensure service safety and compliance.
Competition
Other cloud providers offer comparable services to Elastic Beanstalk. Google Cloud's App Engine (link) provides a fully managed platform that allows developers to deploy applications without managing hardware or infrastructure. Microsoft Azure's App Service (link) offers various app hosting services with support for multiple programming languages, operating systems, and frameworks. Alibaba Cloud's Web App Service (link) provides similar capabilities with a focus on simplifying application deployment and management. Each of these services offers different features and integrations, and the choice depends on specific project requirements and existing cloud service alignments.
By understanding the technical capabilities and limitations of AWS Elastic Beanstalk, developers and IT administrators can make informed decisions about utilizing its features and benefits for their cloud-based applications, considering competition when selecting the most suitable service for their needs.
 AWS Regions
AWS Regions
 AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda
 AWS CodeArtifact
AWS CodeArtifact
 Amazon Lightsail
Amazon Lightsail