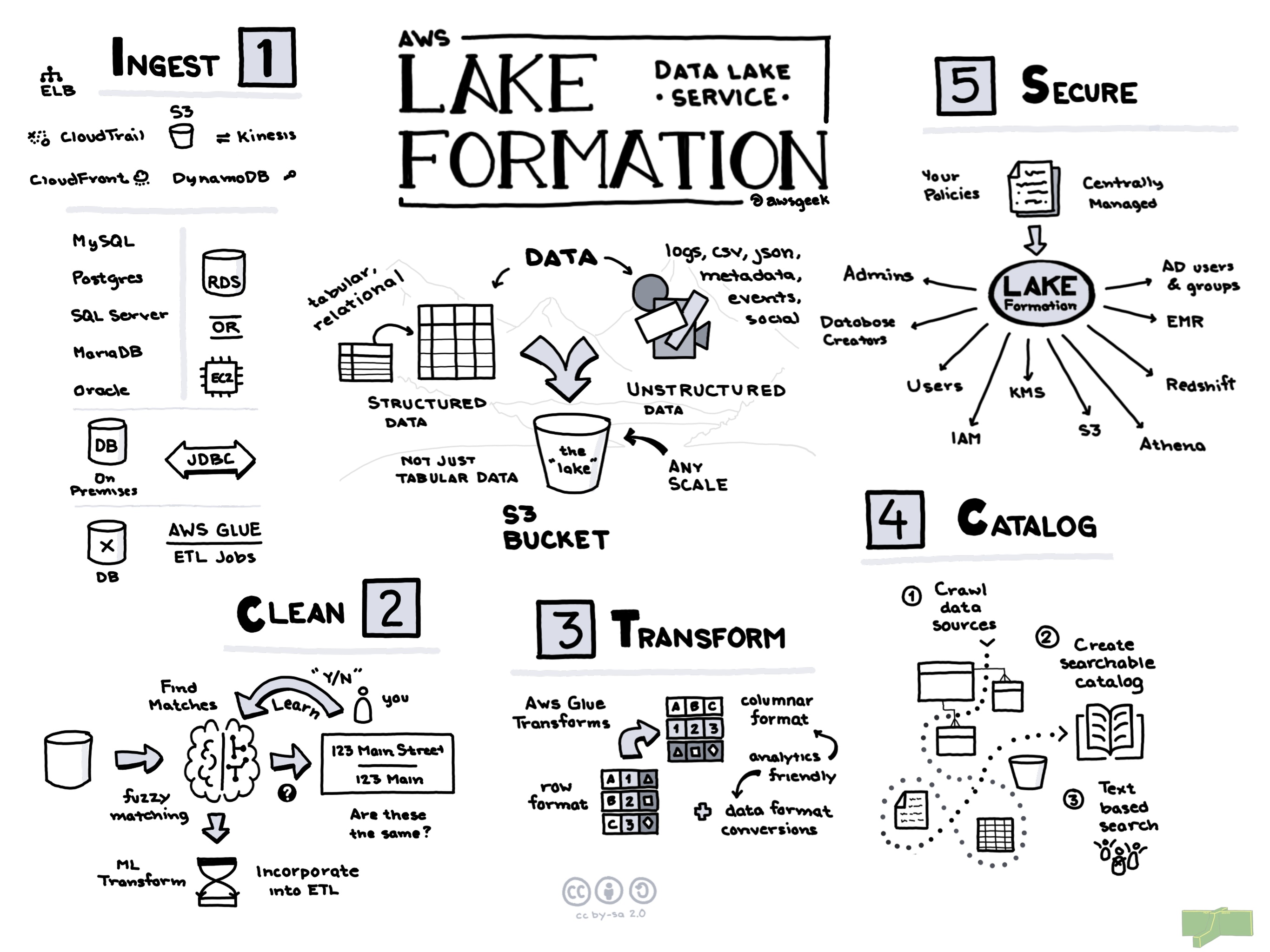
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lake Formation is a service designed to simplify the process of building secure data lakes on AWS, offering a scalable and cost-effective solution for data storage and analytics. A data lake allows organizations to store and analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data at any scale. AWS Lake Formation helps streamline this process by setting up a secure data lake in days instead of months, which can be a game-changer for IT administrators and developers who are looking to leverage massive datasets for business intelligence, machine learning, and real-time analytics.
Use Cases
AWS Lake Formation is versatile and can be adapted to multiple scenarios. One primary use case is analytics and reporting, where businesses analyze large datasets to derive meaningful insights. Data scientists can benefit from using Lake Formation to expedite their machine learning projects by accessing vast amounts of clean and organized data. Similarly, businesses leveraging feature engineering for AI models can ensure data is reliable and consistent. Real-time data processing is another key use case, where Lake Formation allows for efficient ingestion and processing of streaming data, enabling organizations to react to the latest information. Finally, compliance and data governance are vital in industries like finance and healthcare, and Lake Formation aids in meeting stringent regulatory requirements by providing robust security and data management features.
Pricing
AWS Lake Formation operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which is typical of AWS services. There are no upfront costs or minimum fees involved. Users are charged based on the amount of data cataloged, stored, and the duration of time that cataloging and storage mechanisms are utilized. Additionally, data processing and transfer fees associated with other AWS services, such as Amazon S3 for storage or Amazon Athena for interactive query processing, may apply. It's crucial to understand that while Lake Formation automates many data lake tasks, the costs associated with processing and storage are dependent on the services and configurations chosen by the users.
Scalability
AWS Lake Formation is built on the solid infrastructure of AWS, ensuring that it can scale to meet the demands of any workload. It seamlessly handles petabytes of data, allowing users to increase capacity as needed without degradation in performance. This scalability is underpinned by the integration with AWS Glue and other services, facilitating the cataloging, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), and analysis of large volumes of data effectively. Organizations can take advantage of AWS's global network of availability zones, ensuring high availability and resilience of their data operations.
Availability
As with other AWS services, Lake Formation benefits from AWS’s robust global infrastructure, providing high availability and fault tolerance. With data centers situated worldwide, users can replicate their data across multiple regions, thereby enhancing data durability and availability. This is crucial for organizations that require their data operations to be resilient to failures and downtime. Moreover, redundancy and backup solutions are embedded within the service, ensuring data can be recovered in case of unforeseen incidents.
Security
Security in AWS Lake Formation is paramount. It provides a centralized approach to setting up security policies and managing access permissions, which is crucial for protecting sensitive data. The service incorporates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for user access control and enforces encryption both at rest and in transit using AWS Key Management Service (KMS). Additionally, Lake Formation allows for fine-grained access control, enabling administrators to define permissions at the table, column, or row level, ensuring that users only have access to the data necessary for their roles. This rich set of security features makes Lake Formation suitable for industries with stringent compliance and regulatory demands.
Competition
AWS Lake Formation faces competition from similar services across other leading cloud providers. Alibaba Cloud offers a service known as Data Lake Analytics, which provides serverless interactive analytics for a wide variety of data formats and sources. Google Cloud's BigLake, built on top of BigQuery, unifies data warehouses and lakes with integrated governance and performance optimizations. Microsoft Azure offers Azure Data Lake Storage, providing storage optimized for big data analytics and supporting a wide array of data processing frameworks. Each of these services is designed to streamline the creation and management of data lakes while offering unique features suited to their ecosystems.
These competitive solutions vary in integration, pricing, and capabilities, providing developers and IT administrators several options depending on their specific needs and existing technological environments. It's essential for users to assess these services comprehensively to select the one that aligns most closely with their operational requirements and strategic goals.
 Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
 Amazon EMR
Amazon EMR
 AWS Ground Station
AWS Ground Station
 Big Data Architectural Patterns & Best Practices on AWS
Big Data Architectural Patterns & Best Practices on AWS