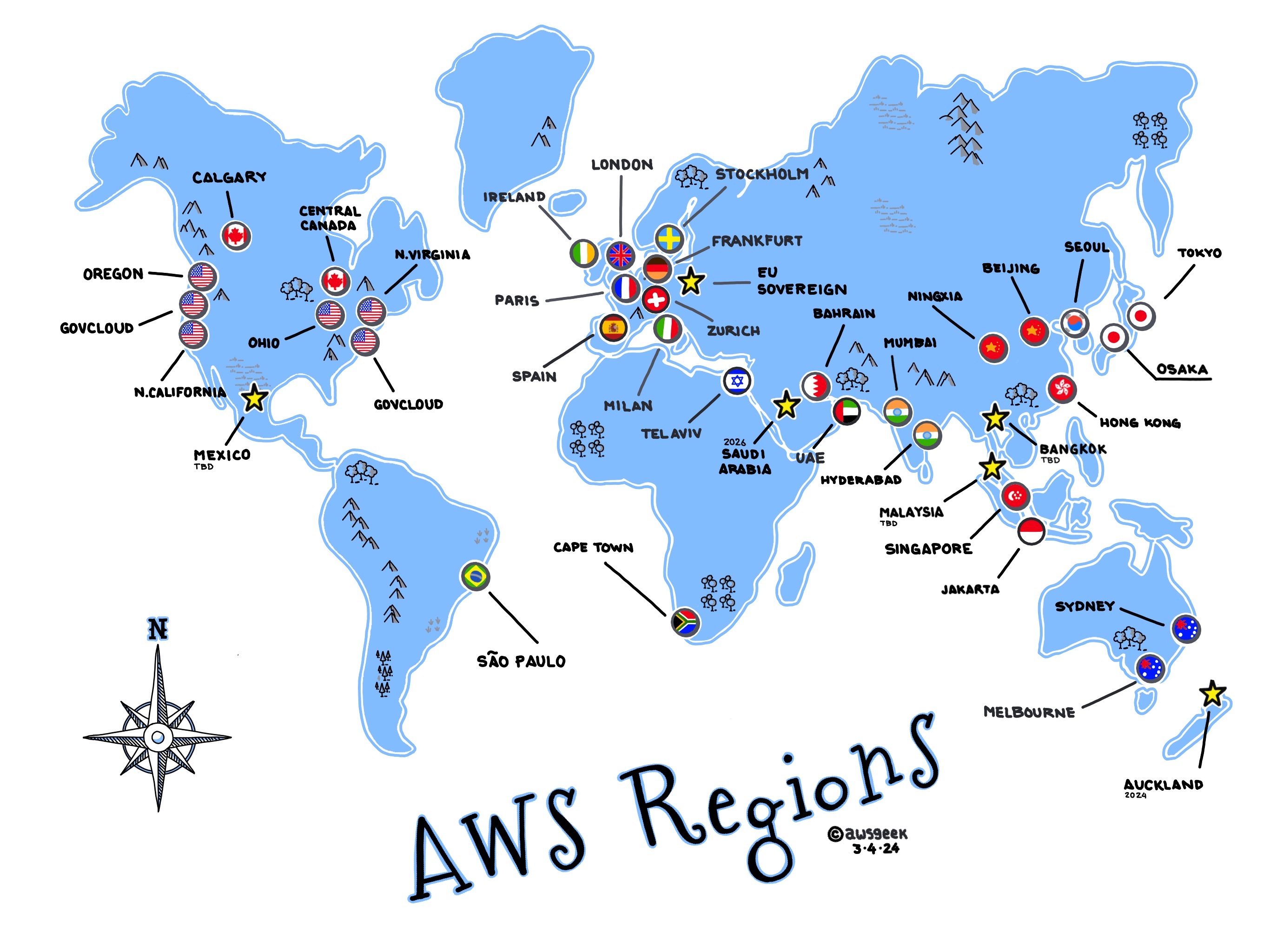
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has established itself as a leading cloud service provider, offering a robust set of global cloud services that allow businesses and developers to deploy applications in a highly scalable and resilient environment. AWS Regions play a crucial role in ensuring that applications run efficiently, quickly, and reliably worldwide. For professional developers and IT administrators, understanding the intricacies of AWS Regions is essential for optimizing the deployment and management of cloud-based applications and services.
Use Cases
AWS Regions are designed to provide developers and companies with the ability to place resources in multiple locations around the globe. This geographic distribution is particularly beneficial for reducing latency, optimizing disaster recovery strategies, and adhering to data sovereignty laws. Use cases for AWS Regions include web and mobile applications that require low-latency user experience, global enterprises needing compliance with local data regulations, and systems requiring robust disaster recovery mechanisms with architecture designed to withstand region-level outages.
Pricing
The pricing for services across AWS Regions can vary depending on the specific region due to factors like operational costs and government levies. It is important for administrators and developers to assess the cost implications of deploying services in different regions, as moving data between regions also incurs additional charges. Tools like the AWS Pricing Calculator can assist in estimating costs based on different regions. AWS provides flexibility in terms of pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing businesses to only pay for the resources they consume without long-term contracts or complex licensing dependencies.
Scalability
AWS Regions are composed of Availability Zones that allow for efficient scaling of applications. The architecture of multiple, isolated locations within an AWS Region promotes high availability and fault tolerance, offering developers the advantage of spreading applications across multiple zones to achieve better redundancy and scalability. Elasticity is a core feature, permitting applications to automatically scale up or down based on demand, which is essential for handling traffic spikes or for workloads with unpredictable or dynamic resource requirements.
Availability
The high availability provided by AWS Regions is grounded in the use of multiple Availability Zones per region. This architecture is critical for developers who are building applications requiring continuous uptime and reliability. AWS Regions are interconnected with low-latency links, ensuring effective communication between zones and regions. In the event of a failure in one Availability Zone, applications can continue to operate effectively without disruption by leveraging other zones within a region.
Security
Security in AWS Regions is approached with a multi-layered strategy, ensuring that data and applications are protected from evolving threats. AWS employs robust security measures including data encryption, access management, and regular security audits. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows for fine-grained control over who can access specific resources. Each AWS Region is ISO 27001, SOC 1, and SOC 2 compliant, among other certifications, which ensures adherence to international standards for data protection and privacy.
Competition
The cloud services market includes formidable competitors such as Alibaba Cloud, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure, each providing similar regional distributions to enhance latency and compliance requirements.
Alibaba Cloud offers Global Infrastructure with a wide range of regions in Asia, Europe, and the Americas, tailored for digital business expansion and compliance with local regulations.
Google Cloud provides Regions and Zones that allow customers to run applications closer to their users and meet high availability requirements by deploying across multiple zones.
Microsoft Azure's Regions span a vast array of locations worldwide, offering resilient and compliant services that cater to both enterprise and developer needs.
Understanding the various elements of AWS Regions empowers IT administrators and developers to craft applications that are secure, performance-optimized, and cost-efficient. By leveraging AWS Regions effectively, teams can enhance the deployment and management of their global applications in a way that aligns with business objectives and user expectations.
 AWS re:Invent Keynotes from 2012 to 2020
AWS re:Invent Keynotes from 2012 to 2020
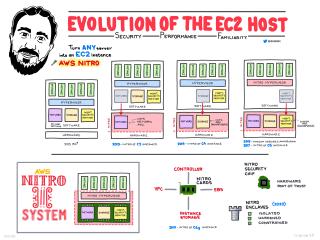 The Evolution of the EC2 Host
The Evolution of the EC2 Host
 Periodic Table of Amazon Web Services
Periodic Table of Amazon Web Services
 Periodic Table of Amazon Web Services
Periodic Table of Amazon Web Services