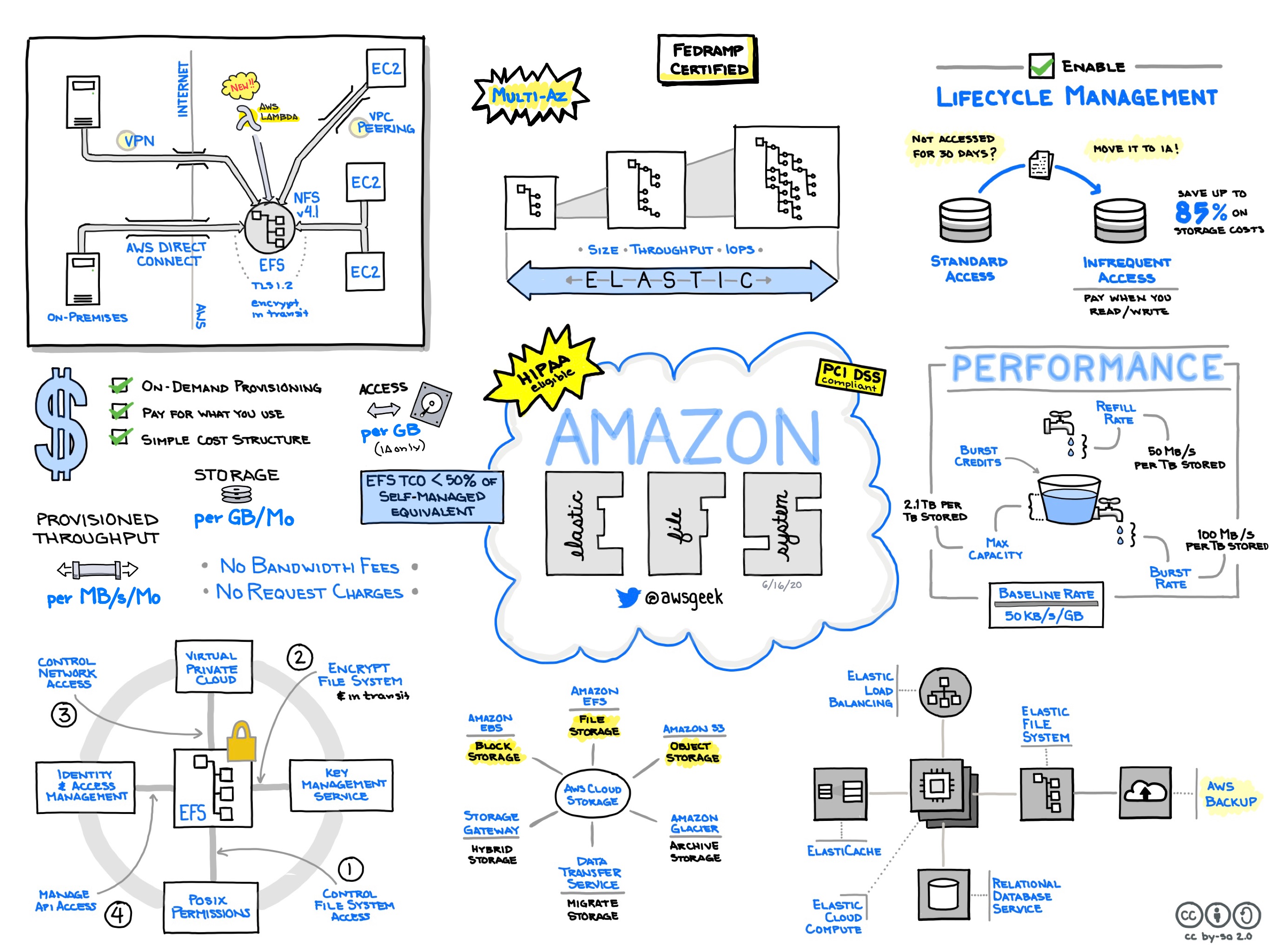
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is a managed file storage service designed to be used with Amazon EC2. It offers a simple, scalable, and elastic NFS file system accessible from multiple EC2 instances simultaneously. This makes Amazon EFS suitable for a variety of workloads requiring shared data access, such as content management systems, big data analytics, and development environments.
Use Cases
Amazon EFS is especially beneficial for applications that require highly scalable file storage. Development and test environments can utilize its compatibility with thousands of connections. Content management systems and media workflows benefit from its ability to handle high throughput and variable workloads. Big data and analytics workloads can utilize its distributed file storage characteristic, which optimally supports data-heavy cloud applications by distributing traffic across storage servers. EFS also supports container-based applications via Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS, allowing shared storage among container instances.
Pricing
The pricing for Amazon EFS is straightforward. You pay for the amount of data storage used per month, with additional charges for requests. EFS offers two storage classes: Standard and Infrequent Access (IA). IA provides a lower cost for files not accessed often, allowing for cost optimization based on access frequency. Pricing can also vary based on the region and data transfer out of EFS to destinations outside AWS.
Scalability
Amazon EFS is designed with elasticity in mind, automatically scaling to accommodate petabytes of data without any provisioning or configuration necessary. Its architecture transparently handles the demands of high throughput and IOPS, dynamically distributing file system data across multiple Availability Zones to ensure consistent performance at scale. Given the unpredictable nature of workloads in modern computing environments, this scalability can dramatically simplify capacity planning for development teams.
Availability
Amazon EFS is built to be highly available, storing data redundantly across multiple Availability Zones within an AWS region. This design provides fault tolerance and ensures data durability. EFS also offers lifecycle management features to automatically move files between storage classes, optimizing for cost, which adds another layer of redundancy based on usage patterns. Its integration with AWS services like AWS Backup further enhances its data protection capabilities.
Security
Security is a priority in the design of Amazon EFS. It integrates with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access and offers encryption both at rest and in transit. This ensures that data is protected from unauthorized access when stored and during transfer between applications and the file system. Network traffic is managed within your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) using security groups, and logging can be enabled via AWS CloudTrail for monitoring access patterns and audits.
Competition
Several cloud providers offer similar managed file storage services. Alibaba Cloud Apsara File Storage NAS offers scalable file storage that supports both NFS and SMB protocols, designed for enterprise applications with high throughput needs. Google Cloud Filestore provides a high-performance file storage service that integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud services, suitable for latency-sensitive applications. Microsoft Azure Files provides file shares in the cloud that can be accessed using the SMB protocol, allowing for easy sharing between applications running on Windows and non-Windows systems. Each of these services offers unique features and capabilities, aligning with the specific needs and infrastructure preferences of organizations seeking cloud-based storage solutions.
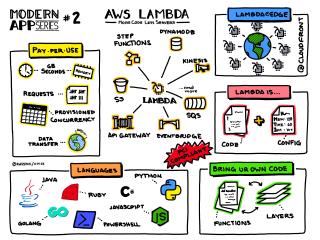 AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda
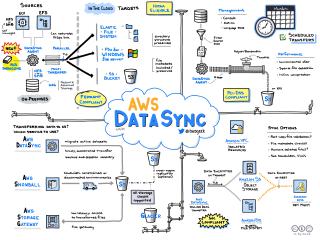 AWS DataSync
AWS DataSync
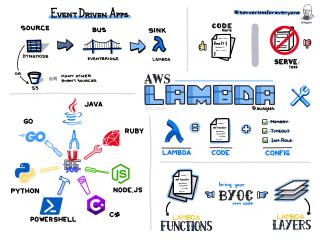 AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda