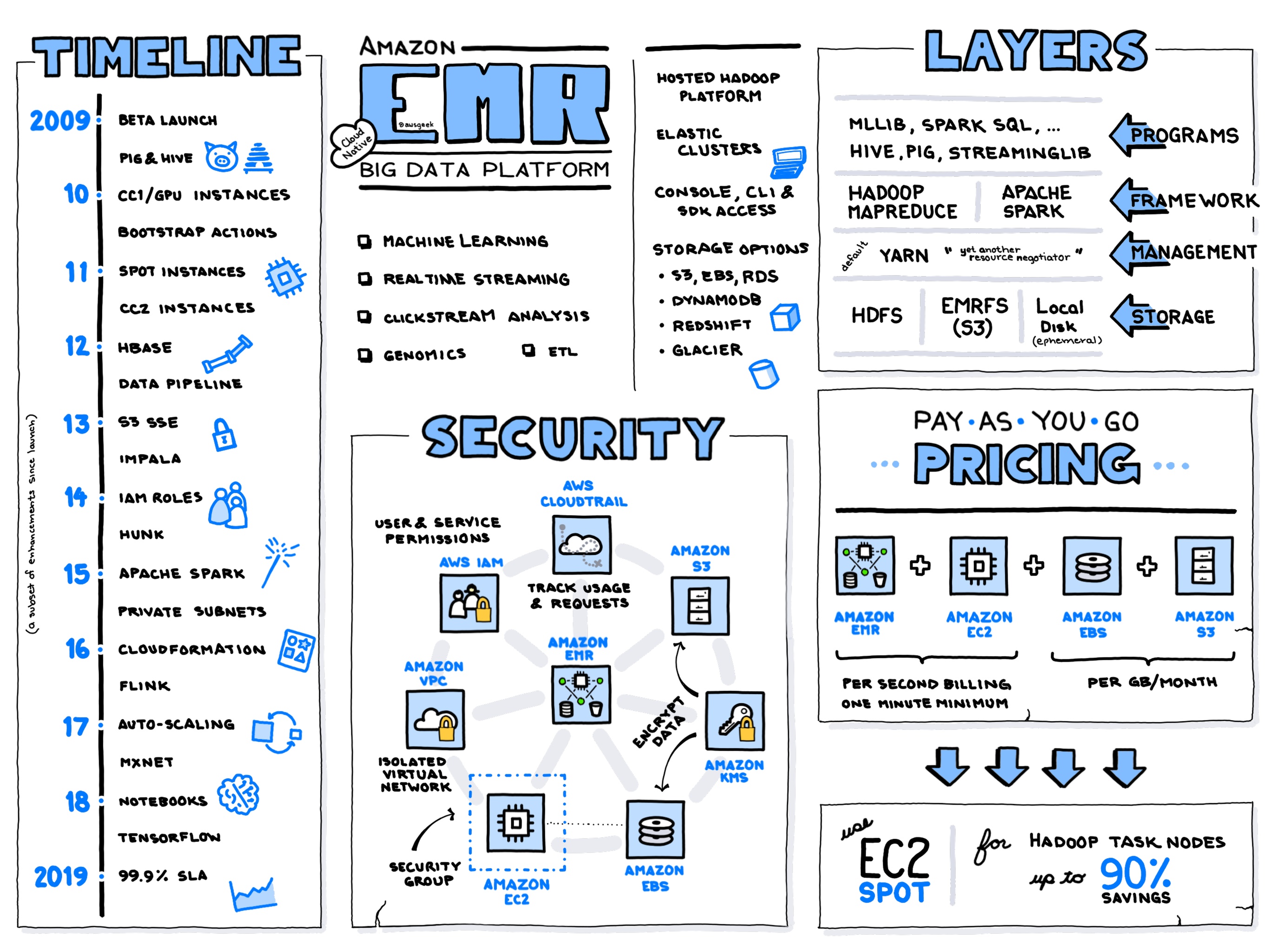
Amazon EMR, short for Elastic MapReduce, is a cloud-native service offered by AWS that facilitates the processing and analysis of vast amounts of data using popular big data frameworks like Apache Hadoop, Spark, HBase, and Flink. Designed to effortlessly scale with your needs, EMR abstracts the complexities of managing on-premises clusters, allowing developers and IT administrators to focus more on their data processing and less on infrastructure maintenance.
Use Cases
Amazon EMR is renowned for its versatility in handling workloads ranging from log analysis, web indexing, data transformations (ETL), machine learning, and bioinformatics to financial analysis. Businesses that require near-real-time analytics on extensive datasets also frequently leverage EMR's capabilities. The platform supports the integration of data with other AWS services such as Amazon S3 for storage, Amazon RDS and Amazon Redshift for relational and data warehouse processing, and AWS Glue for data cataloging.
Pricing
Amazon EMR pricing is primarily based on the underlying EC2 instances that power the EMR cluster and the data storage services that accompany it, such as S3. Users are charged on a per-second basis, which allows for cost efficiency, particularly for transient workloads where clusters can be terminated as soon as processing is complete. The size and number of instances, along with the utilization, will significantly influence the total cost. Additionally, Amazon's Spot Instances can further reduce expenses by allowing users to bid for spare capacity.
Scalability
A significant advantage of Amazon EMR is its scalability. It allows for adding or removing nodes on the fly to meet job-specific requirements. This elasticity ensures that the cluster size can dynamically adjust according to demand, enabling effective management of processing times and costs. EMR can handle workloads of any size by leveraging its underlying infrastructure running on Amazon EC2, which supports both horizontal and vertical scaling strategies.
Availability
Amazon EMR is a highly available service, with multi-AZ deployments ensuring fault tolerance and disaster recovery capabilities. Users can select instances across different availability zones to provide redundancy and failover support. EMR also supports the use of instance fleets that automatically adjust based on the availability of instance types, further ensuring workload continuity even in highly complex environments that demand consistent performance and reliability.
Security
Security in Amazon EMR is robust, incorporating features such as granular IAM policies for resource access control, data encryption at rest and in transit using AWS Key Management Service (KMS), and integration with AWS CloudTrail for auditing purposes. EMR clusters can also be isolated within Amazon VPCs to ensure a secured network environment. Role-based access can restrict actions on both the job and infrastructure levels, thus maintaining strict data governance and compliance standards.
Competition
In the ecosystem of cloud-based big data services, Amazon EMR faces significant competition from similar offerings by other major providers. Google Cloud offers Dataproc, which can be found here. Dataproc allows users to run Apache Hadoop and Spark jobs with rapid instances start-up times and automatic cluster idle monitoring for cost savings. Microsoft Azure provides HDInsight, linked here, which integrates seamlessly with Azure services, supporting common big data frameworks like Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka. Alibaba Cloud's equivalent, E-MapReduce, is described here, providing support for open-source big data ecosystems, tailored towards businesses with specific needs in high-volume data-intensive computations.
Amazon EMR remains a go-to solution for developers and IT administrators seeking to execute large-scale data processing tasks without the need to manage complex infrastructure setups. With its scalable, secure, and flexible environment, it continues to be instrumental in driving big data innovation within various industries.
 Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
 AWS Lake Formation
AWS Lake Formation
 AWS Ground Station
AWS Ground Station
 Big Data Architectural Patterns & Best Practices on AWS
Big Data Architectural Patterns & Best Practices on AWS