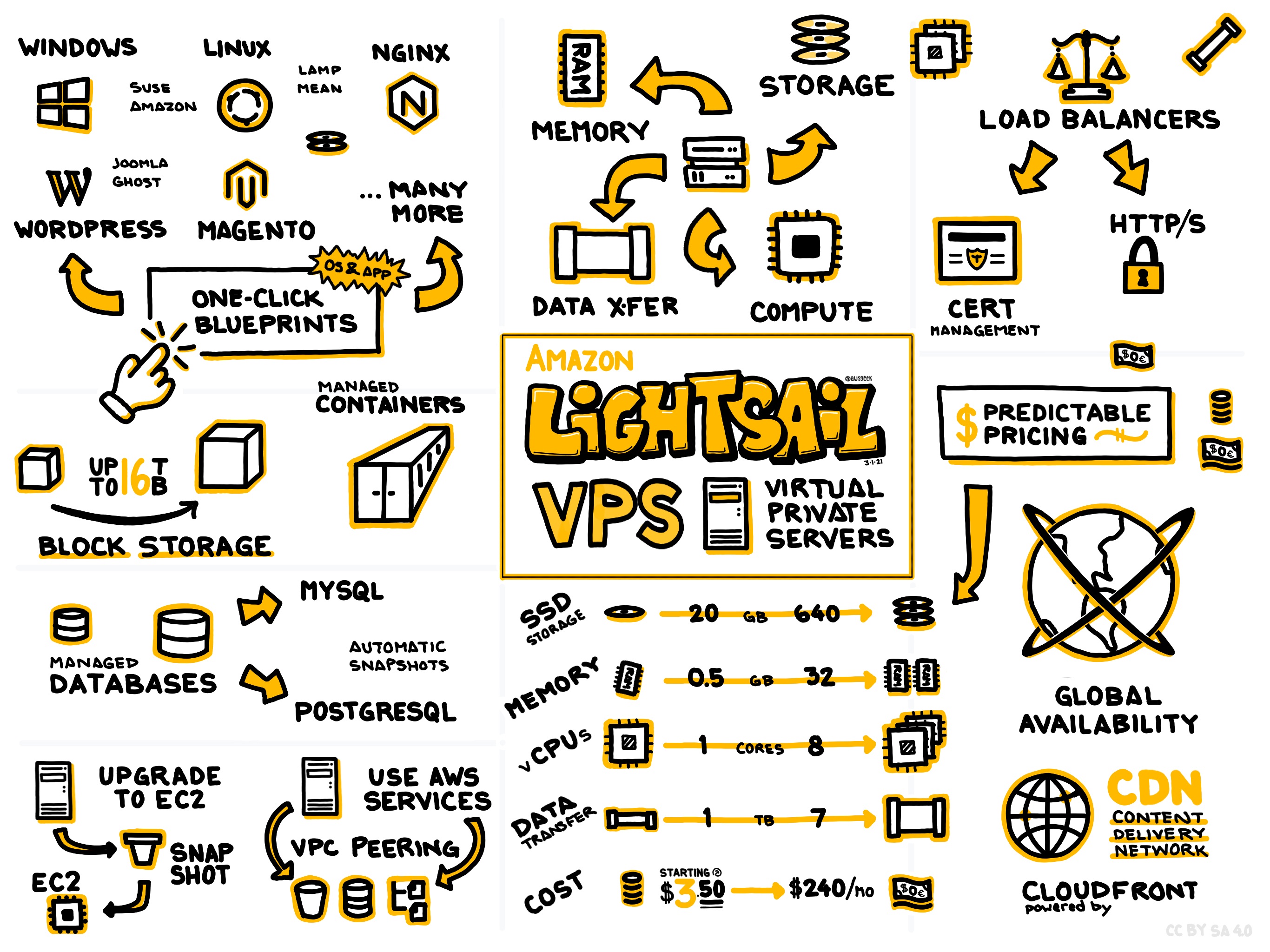
Amazon Lightsail is a cloud computing service designed for developers and IT professionals looking for a straightforward, cost-effective environment to deploy and manage applications. It offers virtual private servers (VPS), managed databases, and networking. Lightsail is particularly beneficial for those who want to deploy simple workloads like web applications, blogs, or development environments without dealing with the complexities of larger AWS services.
Use Cases
Amazon Lightsail is ideal for small to medium-sized projects that require straightforward infrastructure. Common use cases include hosting static websites, launching simple web applications such as WordPress and Joomla, setting up e-commerce platforms, and creating test or development environments. Its simplicity makes it a good fit for educational purposes, allowing developers to experiment with cloud resources without incurring significant costs. Developers who require more extensive network configurations or intricate resource management might find broader AWS services like EC2 more suitable.
Pricing
Lightsail pricing is predictable, with fixed monthly rates that vary based on the resources allocated. Users can select from several predefined plans ranging from basic configurations with 512 MB of RAM and low CPU allocations to more robust setups with up to 32 GB of RAM and higher network transfer limits. The pricing structure is transparent, enabling businesses to anticipate their monthly expenses without hidden costs. Additionally, Lightsail offers a free tier for testing and development, which includes 750 hours of usage per month for the first three months.
Scalability
While Amazon Lightsail is excellent for projects with modest demands, it does come with constraints that might limit its appeal for more extensive deployments. It provides easy instance scaling where users can transfer data between Lightsail servers or upgrade their resources; however, scaling mechanisms are not as extensive as those found in Amazon EC2. The service does include load balancers and storage options through block storage, but for truly scalable enterprise solutions, one might need to consider migrating to other AWS services.
Availability
Lightsail benefits from Amazon’s established infrastructure, and VPS instances are deployed within AWS Regions and Availability Zones. This distribution contributes to high availability and reliability. However, it's important to note that Lightsail users have less granular control over geographical failures compared to other AWS services. Reliability in tandem with regular backups ensures that Lightsail can maintain operations during outages, although the service-level agreement (SLA) is not as comprehensive as other AWS solutions.
Security
Amazon Lightsail incorporates AWS’s robust security features, ensuring that data and applications are protected. These features include data encryption in transit using SSL/TLS, key management with AWS Key Management Service (KMS), and firewall management capabilities to control traffic to your instances. Lightsail also integrates smoothly with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), enabling detailed permission settings for various roles. Unlike more comprehensive AWS services, however, Lightsail offers limited configurations for advanced security features such as VPNs, which might be a consideration for enterprises handling sensitive data.
Competition
In the realm of straightforward VPS solutions, several cloud providers offer competing services. Google Cloud has Compute Engine, offering a similar set of features with flexible resources and pricing. Microsoft Azure provides Azure Virtual Machines which support a wider range of operating systems and greater granularity in scaling. Alibaba Cloud’s counterpart is Elastic Compute Service (ECS), focusing on scalable virtual servers. Each of these platforms brings distinct advantages and specific integrations, making them worthy considerations depending on particular project needs and existing technological ecosystems.
By understanding the capabilities and limitations of Amazon Lightsail, developers and IT administrators can make informed decisions on deploying applications, weighing the simplicity and cost-effectiveness against scalability and advanced features offered by other AWS and non-AWS services.
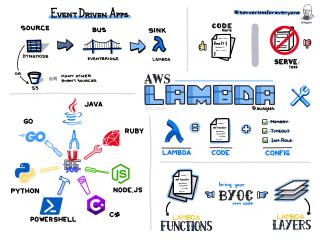 AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda
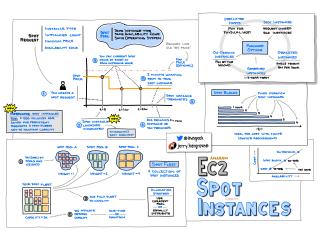 Amazon EC2 Spot Instances
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances